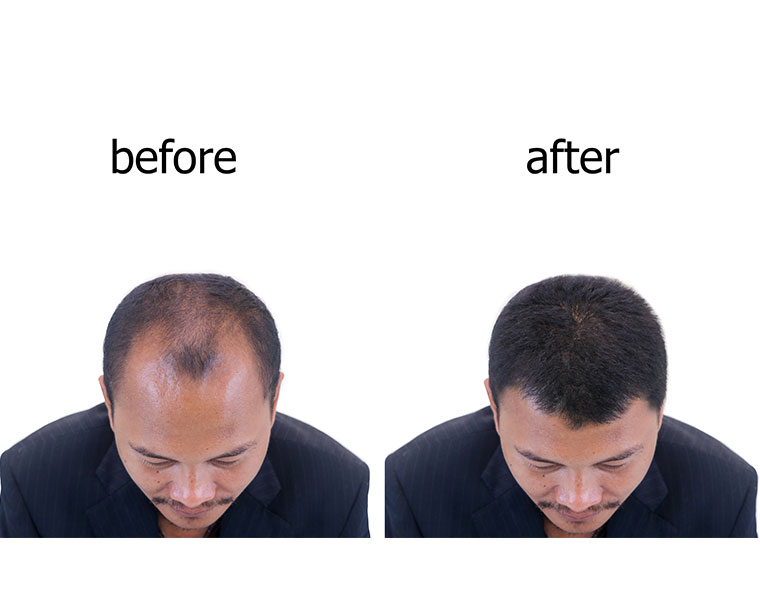
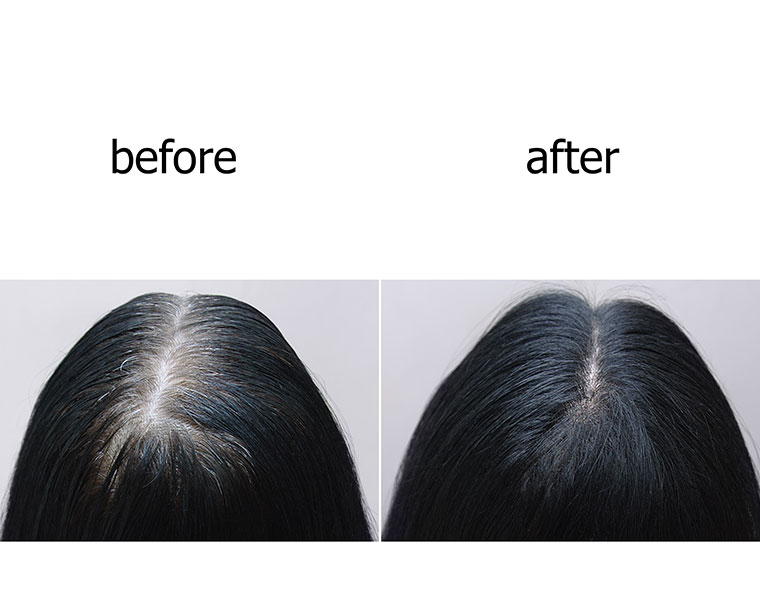
Because of significant surgical advances with improved results, interest in hair replacement surgery has increased significantly during the past decade. Hair loss affects two out of every three men, and one in five women. Some people begin to lose hair in their twenties. Frequent shampooing, poor circulation, wearing hats or any other personal habits are not factors that cause hair loss. For men, heredity is the major factor in hair loss. For women, hormonal changes, including those that occur in menopause, are mainly responsible for female “pattern changes,” which include thinning and loss. Accidents, burns, and disease can also trigger hair loss. The key factor in hair replacement is the presence of donor hair on the side or the back scalp, which is then used to replace hair where loss has occurred. Total baldness makes replacement surgery impossible. Hair quality is another factor. Light-colored hair, as well as coarse-textured hair, produce a look of greater density than fine or dark hair.
As with all facial plastic surgery, good health and realistic expectations are prerequisites. Understanding the limitations of the surgery is crucial. No ideal in hair replacement surgery exists. The goal is to improve your appearance as much as possible. Before deciding on hair replacement surgery, ask your facial plastic surgeon to explain the options available for your particular type of hair loss.
Male pattern baldness often begins with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, and is the easiest condition to correct. It is progressive over a lifetime and is a major consideration for your surgeon. Hair replacement surgery frequently requires multiple grafts of hair being implanted during multiple sessions, generally spacing each session at least four months apart to allow for adequate healing.
The surgeon will explain which type of anesthesia is indicated. Facial plastic surgeons usually decide on a local or twilight anesthesia for grafting, but many surgeons choose general anesthesia for the more involved surgical procedures for replacing hair. The surgical facility to be used will also be determined by the extent of the procedure.
It is not essential to be bald or nearly bald before undertaking hair transplantation. Age also is no contraindication for hair transplantation. The younger the person, though, the more conservative the approach must be for transplantation, because the permanent donor site may not yet be established. Ideally, the patient should have dense growing hair in the donor sites to sufficiently fill any present or future areas of baldness.
The color of the hair in contrast to the skin color will be discussed with you by your surgeon. The texture of your hair, coarse or fine, will also determine the final result in hair transplantation.
However, the patients most satisfied with hair transplantation are those who will accept the estimate of improvement as given by the surgeon.
If you opt for surgery, your surgeon will describe the technique indicated, the type of anesthesia to be used, the surgical facility, any additional surgery, and risks and costs.
The most commonly known hair replacement surgery requires taking a strip of hair-bearing scalp from the back of the head. The strip is then divided into several hundred smaller grafts. These grafts are then inserted into tiny slits in the scalp, and must be placed in such a way that hair all grows in the same, natural direction. While some of the grafts may contain up to five or six hairs, it is sometimes necessary to use a number of grafts containing only one or two hairs to create a natural appearance. This is known as mini- and micrografting.
Skin flap surgery is another efficient technique used to cover balding areas. After a piece of bald scalp is removed, a section of hair-covered scalp is moved and sutured into place. Scars are generally covered by new hair growth. Bald spots at the crown of the head can be covered by removing the hairless area of skin and then stretching the hair-covered scalp adjacent to the bald spot over the opening. This is known as scalp reduction surgery.
A newer technique involves the use of tissue expanders. This allows stretching of the skin which aids in the reduction of the size of the bald scalp.
After surgery, your surgeon may choose to apply a dressing for a day or two. If stitches are used, they are usually removed within 10 days. The second or third day after surgery, you will probably be allowed to shampoo. Your head and scalp may feel tight with some aching, but this can be controlled by medication. It is crucial that you follow the instructions for post-operative visits and care. Swelling or bruising in the area treated is likely. Cold compresses may be recommended by the surgeon.
The newly transplanted hair often falls out in the six weeks following the procedure. This, however, is absolutely normal. New hair growth will take about six to 12 weeks to develop. To attain a look of natural hair growth, it is often necessary to fill in patchy areas, adjust the hairline, or remove excess tissue from areas that have been treated with flap surgery. These touch-up procedures are to be expected and are an essential part of the whole picture of hair replacement surgery.